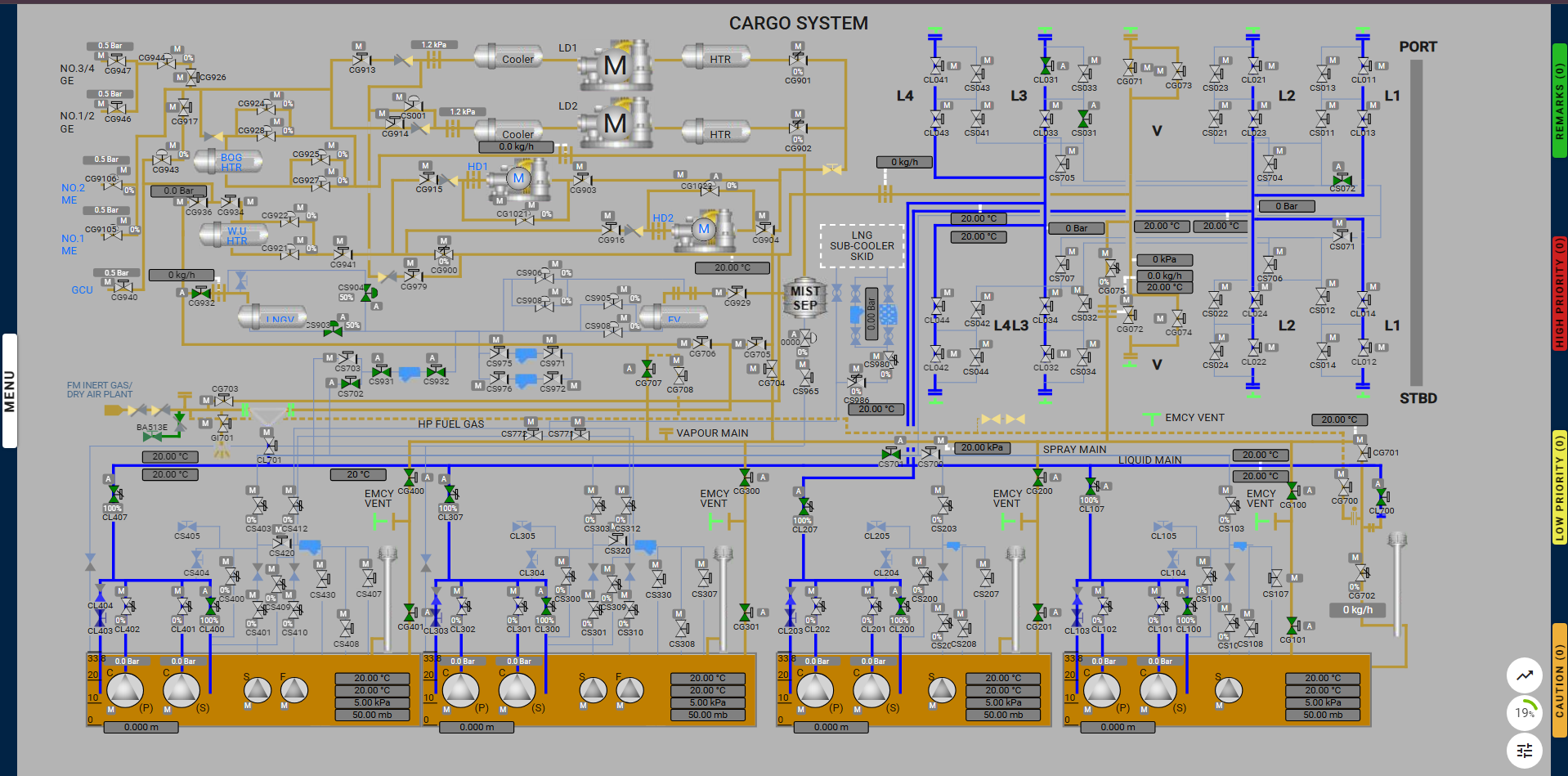
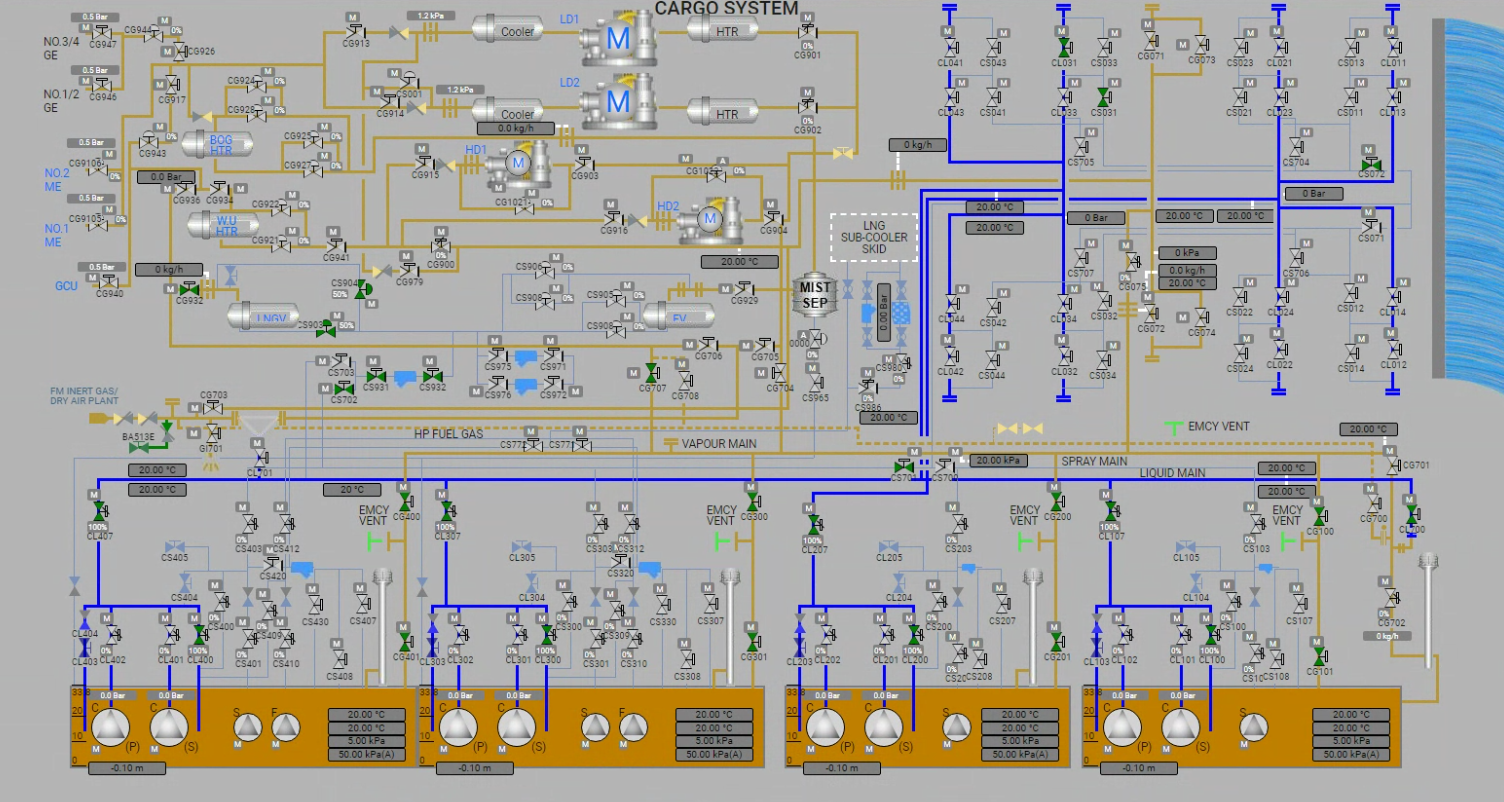
Function: Replacement of inert gas in cargo tanks with LNG vapour
The purpose of gassing-up cargo tanks is to remove the inert gas contained within the cargo tanks because inert gas contains approximately 15% carbon dioxide which will freeze at approximately -60°C and produce a white powder that can block valves, filters, and nozzles.
LNG liquid is supplied from the terminal to the liquid manifold where it passes to the spray line via an ESD liquid manifold valve to the vessel’s LNG vaporizer. It is then delivered as LNG vapor into the top of the cargo tanks via the vapor line and exits from the cargo tank via the filling lines. From here it can be vented to the atmosphere via the No.1 vent mast for step one of the process. Step two then follows with the LNG vapor being returned to the terminal using a high-duty (HD) compressor.
In some instances venting to the atmosphere is not permitted so options available include sending the vapor to the terminal, using the vapor as a gas fuel supply for the generator engines, or sending it for gas burning in the Gas Combustion Unit (GCU); or a combination of these choices.
It should be noted that the level of methane vented into the atmosphere is dependent upon the terminal regulations, which should be discussed and agreed upon before operations commence.
Performance criteria
Auxiliaries involved
Operation duration
Necessary device
Checkpoints
This exercise is carried out onboard an LNG carrier, where liquid LNG is provided by the shore and converted into vapor using onboard LNG vaporizer equipment. The LNG vapor is then introduced into the cargo tanks from the top, replacing the heavier inert gas present inside the tanks. The inert gas is extracted from the bottom of the tank and released into the atmosphere.
The exercise is divided into two main steps:
Setting up the correct configuration of emergency shutdown systems. Starting the manifold water curtain. Preparing gas measurement instruments for use. Preparing the LNG vaporizer. Opening the required valves and connecting the necessary hoses (or “spool pieces”).
The assessment begins when the actual flow of LNG starts from the shore. The user must ensure the following during the assessment:
Learning Objectives for the Exercise
Participants will be able to effectively demonstrate the process of gassing up cargo tanks on LNG ships, understanding the safety protocols, operational procedures, and the significance of maintaining safe vapor conditions.
Key Components:
Understanding Gassing Up:
Operational Procedures:
Detail the step-by-step process for gassing up cargo tanks, including:
Monitoring and Verification:
Practical Demonstration:
Assessment Criteria:
By achieving this objective, participants will acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for safely and efficiently gassing up cargo tanks on LNG ships, ensuring safe and effective operations.
Note: To maintain the LNG vaporizer outlet flow, adjust Valve CS903 in combination with the Flow from Shore and
to maintain the vapor-to-atmosphere flow, adjust Valve CG702 as needed.
| Alarm Condition | Alarm Time | Alarm Level | Alarm Title | Alarm Description | Action |
| remark | Preparing Of LNG Vaporizer | Usually, the LNG vaporizer is properly prepared 3 hours before the operation. | |||
| remark | Increase LNG Flow rate | Vapor blocks might be there inside the lines, increasing the LNG flow rate from shore to 15 m³/h. | |||
| remark | Open LNG Vaporizer Bypass valve | Open the LNG Vapourizer Bypass valve immediately. | |||
| remark | Open The Gas Detector | Open the gas detector sampling point on the liquid line in any of the 4 tanks. | |||
| remark | Increase LNG Vaporizer Outlet Temperature | Increase the outlet temperature of the LNG Vaporizer to 40°C. | |||
| remark | Valve CS904 To Auto Mode | Set the valve output value to 40 and change the valve to auto mode. | |||
| caution | Maintain LNG Vaporizer Outlet Vapour | Maintain the LNG vaporizer outlet vapor flow between 5000 kg/h to 6750 kg/h. | |||
| caution | Maintain LNG Vaporizer Flow And Vapour Flow To Atmosphere | Maintain LNG vaporizer outlet flow and vapor flow to the atmosphere between 11500 kg/h to 12500 kg/h. | |||
| caution | Deviation Detected | Deviation from the exercise is detected, undo your last action. |
Step-by-Step Procedure.
1 – Configure the Correct Setting for the ESD
2 – Start the Manifold Water Curtain
3 – Prepare Gas Instruments for Use
4 – Prepare LNG Vaporizer for Use
5 – Connect Manifold Arm Spool Piece
6 – Open Required Valves for Line-Up and Connect Spool Pieces
Open the following valves:
And connect the spool piece below the valve CL700.
7 – Start Gassing-Up with Minimum Flow of 10m³/h
Note: To adjust the flow, enter the desired value in the Flow from Shore field on the control panel. You can also use Valve CS903 in combination with the Flow from Shore to control the flow more effectively.
8 – Achieve 40°C in LNG Vaporizer Outlet Temperature
9 – Check All Gas Sampling Points
10 – Monitor Vapour Outlet No.1 Vent