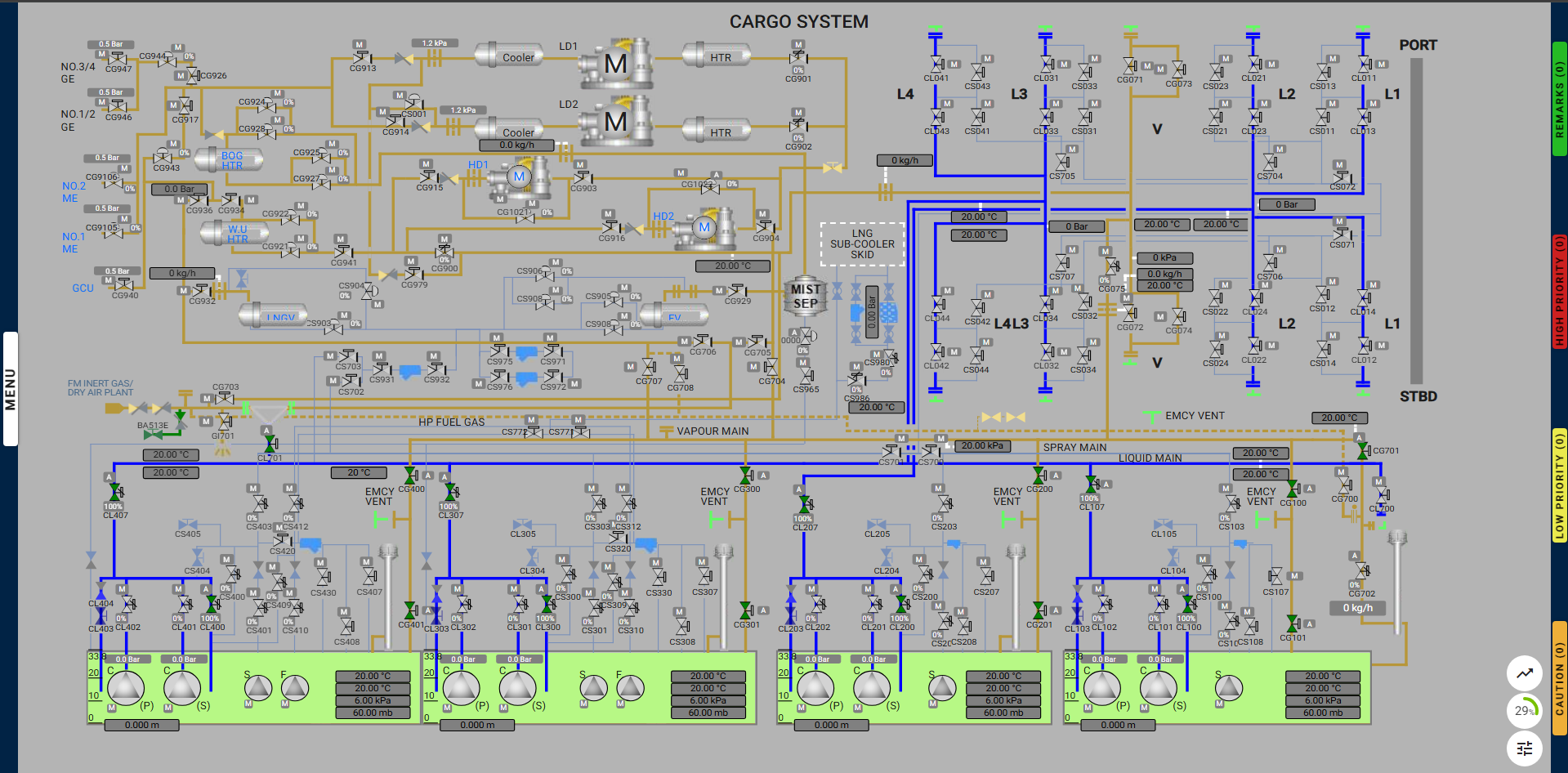
The purpose of Inerting cargo tanks is to remove the oxygen content to avoid the cargo tanks entering the flammable range during gas filling. As part of the process of preparing the cargo tanks ready to carry the next LNG cargo, they must be Inerted with inert gas, thus removing ignition risk when gas filling.
The Inert gas, provided by the vessel’s inert gas generator, should be introduced at the bottom of each cargo tank simultaneously, via the liquid line. The cargo tank atmosphere will be displaced from the top of each cargo tank into the vapor line and discharged to the atmosphere through the No.1 vent mast.
This exercise focuses on preparing the systems and equipment to successfully make the tank atmosphere completely inert. The objective is to ensure that the dry air present inside the tanks is replaced with inert gas, which is generated by the inert gas generator onboard the LNG carrier.
The exercise begins with initial milestones that describe how to set up various equipment, including:
Learning Objectives for the Exercise
Participants will be able to effectively demonstrate the process of inerting cargo tanks on LNG ships using inert gas, understanding safety protocols, operational procedures, and the importance of preventing explosive atmospheres.
Key Components:
1. Understanding Inerting:
2. Operational Procedures:
Detail the step-by-step process for inerting cargo tanks, including:
3. Monitoring and Verification:
4. Practical Demonstration:
Assessment Criteria:
By achieving this objective, participants will gain the necessary knowledge and skills to safely and efficiently inert cargo tanks on LNG ships, enhancing overall safety and operational integrity.
Milestones:
| Alarm Condition | Alarm Time | Alarm Level | Alarm Title | Alarm Description | Action |
| Supply Started | remark | Inerting Of Cargo Tanks Started | Inerting of the cargo tanks has started. | ||
| On Inerting completed | remark | Inerting of tanks completed | Inerting of cargo tanks is completed, stop the delivery of inert gas. | ||
| On Inerting completed | remark | Check the sampling point on vapour line | Check the sampling point on vapour line for dry air properties, in all cargo tanks. | ||
| Stopped delivery of inert gas | remark | Close Valve CG702 | Inerting of tanks is stopped, close the valve CG702. | ||
| started delivery of Inert gas | remark | Open Valve CG702 | Open the valve CG702, to vent out the dry air. | ||
| During inerting process | caution | Maintain IGG Outlet Flow And Outlet Flow To Atmosphere | Maintain IGG outlet flow and outlet flow to atmosphere between 15500 kg/h to 16500 kg/h. | ||
| During exercise | caution | Deviation Detected | Deviation from the exercise is detected, undo your last action. |
Step By Step Procedure:
Proper Line Up For Inerting: