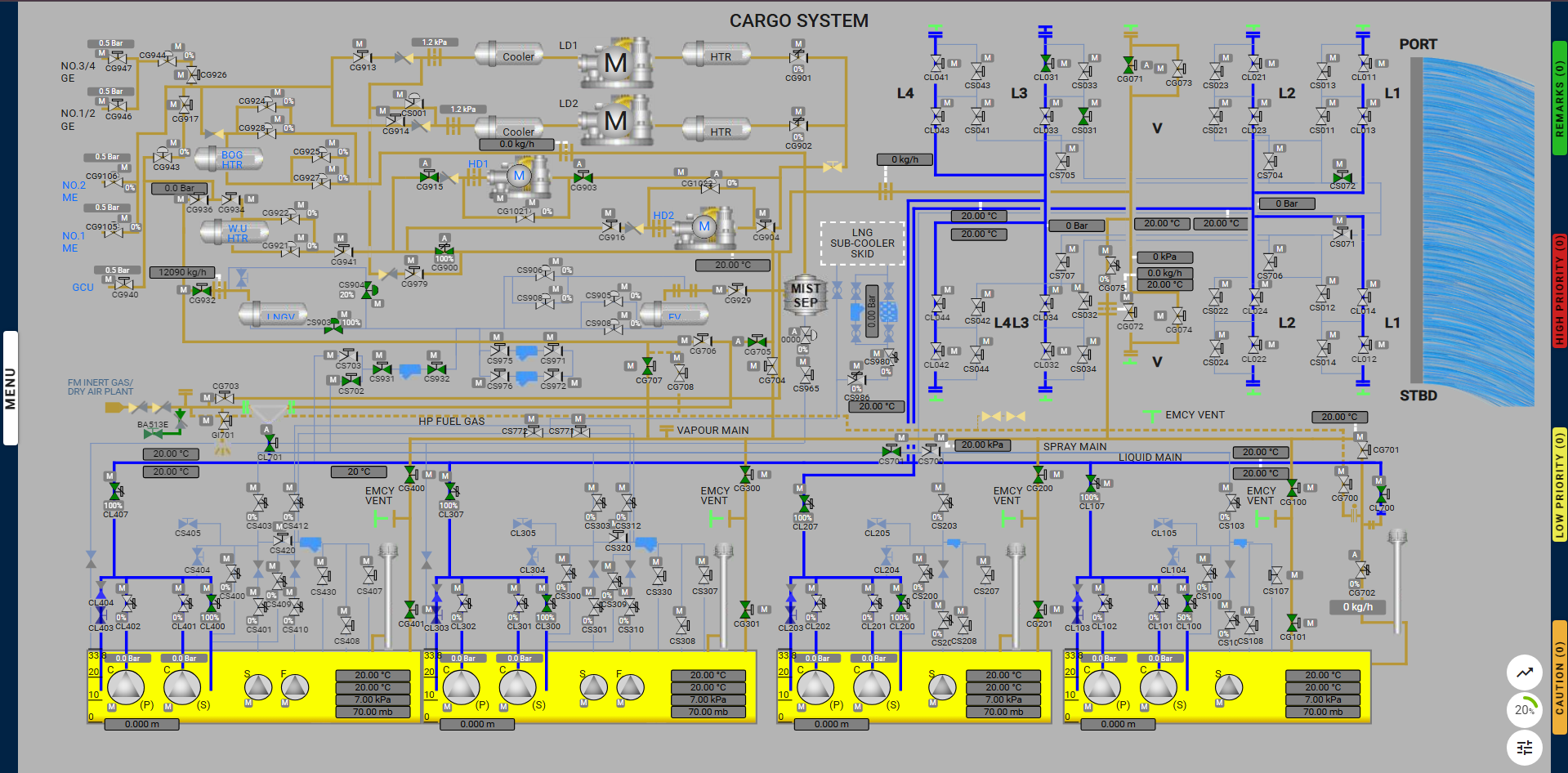
This exercise is carried out onboard an LNG carrier, where liquid LNG is provided by the shore and converted into vapor using onboard LNG vaporizer equipment. The LNG vapor is then introduced into the cargo tanks from the top, replacing the heavier inert gas present inside the tanks. The inert gas is extracted from the bottom of the tank and released into the atmosphere.
The exercise is divided into two main steps:
Setting up the correct configuration of emergency shutdown systems. Starting the manifold water curtain. Preparing gas measurement instruments for use. Preparing the LNG vaporizer. Opening the required valves and connecting the necessary hoses (or “spool pieces”).
The assessment begins when the actual flow of LNG starts from the shore. The user must ensure the following during the assessment:
Learning Objectives for the Exercise
Participants will be able to effectively demonstrate the process of gassing up cargo tanks on LNG ships, understanding the safety protocols, operational procedures, and the significance of maintaining safe vapor conditions.
Key Components:
Understanding Gassing Up:
Operational Procedures:
Detail the step-by-step process for gassing up cargo tanks, including:
Monitoring and Verification:
Practical Demonstration:
Assessment Criteria:
By achieving this objective, participants will acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for safely and efficiently gassing up cargo tanks on LNG ships, ensuring safe and effective operations.
|
Alarm Condition |
Alarm Time | Alarm Level | Alarm Title | Alarm Description | Action |
| remark | Reduce LNG Vaporizer Outlet Temperature |
Reduce The Outlet Temperature of LNG Vaporizer to 20°C. |
|||
| remark | Change Valve CS904 To Auto Mode | Set the valve output set value to 20 and change the valve to auto mode. | |||
| caution | Maintain Vapour To Shore | Maintain the vapour flow to shore between 5000 kg/h to 6000 kg/h. | |||
| caution | Maintain LNG Vaporizer Flow And Vapour Flow To Shore | Maintain LNG vaporizer outlet flow and vapour flow to shore between 11500 kg/h to 12500 kg/h. Adjust the veins of HD Compressor to maintain vapour flow to shore. | |||
| caution | Deviation Detected | Deviation from the exercise is detected, undo your last action. |
Step-by-Step Procedure
Milestone 1 – Connect Manifold Arm L3, V
Milestone 2 – Open Required Valves for Line-Up and Connect Spool Pieces
Milestone 3 – Prepare HD Compressor and Generators for Use
Milestone 4 – Start the HD Compressor
Once the above prerequisites are met, the “Resume Gassing Up” button will become available on the control panel. Click this button to continue the gassing up process.
Milestone 5 – Monitor Cargo Tank Pressure