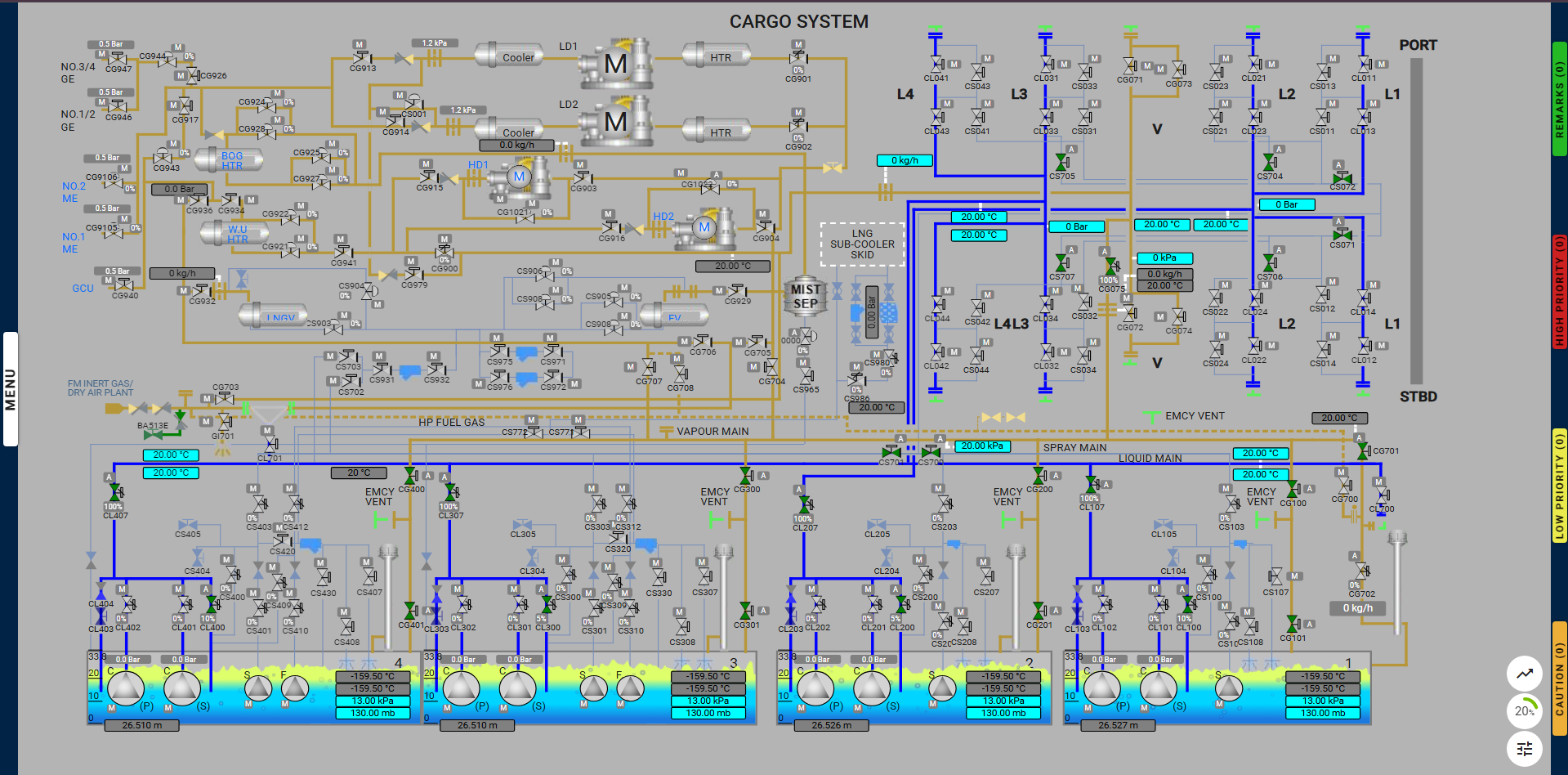
The Line Cool-Down at Sea operation is carried out while the vessel is en route to the discharge port. The goal is to keep the liquid lines at the required low temperature and ensure they are in a ready-to-discharge condition upon arrival. To maintain the liquid lines in a cold state, the vessel uses the spray pumps inside the cargo tanks to guide the LNG from the spray line into the liquid line, thereby cooling it down. This process ensures the lines remain cold and are ready for the custody transfer system upon arrival.
| Function | Lowering cargo line temperature before LNG transfer |
| Performance criteria | Cargo line temperature -100°C |
| Auxiliaries involved | Stripping/spray pump |
| Operation duration | 2 hours |
| Check points | Cargo line temperature sensors and visual frosting and icing |
The purpose of cooling down the LNG lines is to avoid thermal shock on the piping and associated valves which would occur if gradual cooling was not employed.
Therefore, before unloading LNG from the cargo tanks, the cargo liquid lines, crossovers, and cargo filling lines must be cooled down to cryogenic temperatures and this can be undertaken with LNG supplied from the vessel’s cargo tanks.
The cargo tanks will normally be at approximately -160ºC during a loaded voyage with fully loaded cargo tanks and with the supply of fuel gas for the Main Engines (ME) and the Generator Engines (GE).
A stripping/spray pump is used to supply an initial slow flow of LNG to the spray line and crossover into the cargo lines and to the cargo tank filling lines. The operation would normally be undertaken prior to arrival at the port.
The exercise begins by starting the required generators for use. The system is correctly lined up by opening the necessary valves. The spray pump is started, and parameters are verified to ensure the system is functioning properly.
Learning Objectives for the Exercise
Participants will be able to effectively demonstrate the process of cooling down the liquid header on LNG ships prior to discharging, understanding the necessary safety protocols, operational procedures, and the importance of achieving appropriate temperatures for safe LNG transfer.
Key Components:
1. Understanding Liquid Header Cool Down:
o Explain the purpose of cooling down the liquid header to prepare for safe discharging of LNG.
o Identify the risks associated with temperature differentials and the significance of thermal management.
2. Operational Procedures:
o Detail the step-by-step process for cooling down the liquid header, including:
Pre-cool down checks and preparation of systems.
Controlled introduction of cold LNG or nitrogen into the header.
Monitoring temperature and pressure throughout the cooling process.
o Explain how to manage flow rates to prevent rapid temperature changes and ensure system integrity.
3. Monitoring and Verification:
o Demonstrate the use of temperature gauges and pressure monitoring systems during the cool down process.
o Describe how to confirm that the liquid header is within safe operational temperature limits before discharging.
4. Practical Demonstration:
o Simulate the cool down process in a controlled environment or through hands-on training exercises.
o Role-play scenarios to address potential challenges or deviations from the procedure.
Assessment Criteria:
• Ability to articulate the significance of cooling down the liquid header prior to discharging.
• Accurate execution of the cool down procedure and effective monitoring.
By achieving this objective, participants will gain the knowledge and skills necessary for safely and efficiently cooling down the liquid header on LNG ships, ensuring safe operations during discharging.
| Alarm Condition | Alarm Time | Alarm Level | Alarm Title | Alarm Description | Actions |
| remark | Started Line Cooldown | Started cooling the liquid lines. | |||
| caution | Open Filling Valves | Keep the filling valves CL100 and CL400 open. | |||
| remark | Increase Spray Pump Flowrate | Increase and maintain spray pump flow rate between 50 to 55. | |||
| caution | Close Tank Filling Valves | Close the filling valves CL200, CL300, and CL400. | |||
| caution | Close All Filling Valves | Close filling valves CL100 and CL400. | |||
| remark | Line Cooldown Completed | The spray pump can be stopped. | |||
| caution | Open Cargo Tank 4 Valves | Keep valves CS400 and CS404 open. | |||
| caution | High Cross Over Pressure | High cross over pressure in liquid lines, open filling valve CL400. | |||
| caution | Close Valve CL400 | Close filling valve CL400 to fill up the liquid line. | |||
| caution | Deviation Detected | Deviation from the exercise is detected, undo your last action. |
Step By Step Procedure
Open All Required Valves for Line-Up:
Prepare Required Generators for Use:
Start the Spray Pump in Cargo Tank 4:
Starting the Line Cooldown:
Actions at the 3-Minute Mark:
Managing Crossover Pressure at 4 Bar:
Pressure Management:
Actions at the 12-Minute Mark:
At the 14-Minute Mark:
Completion of the Exercise: