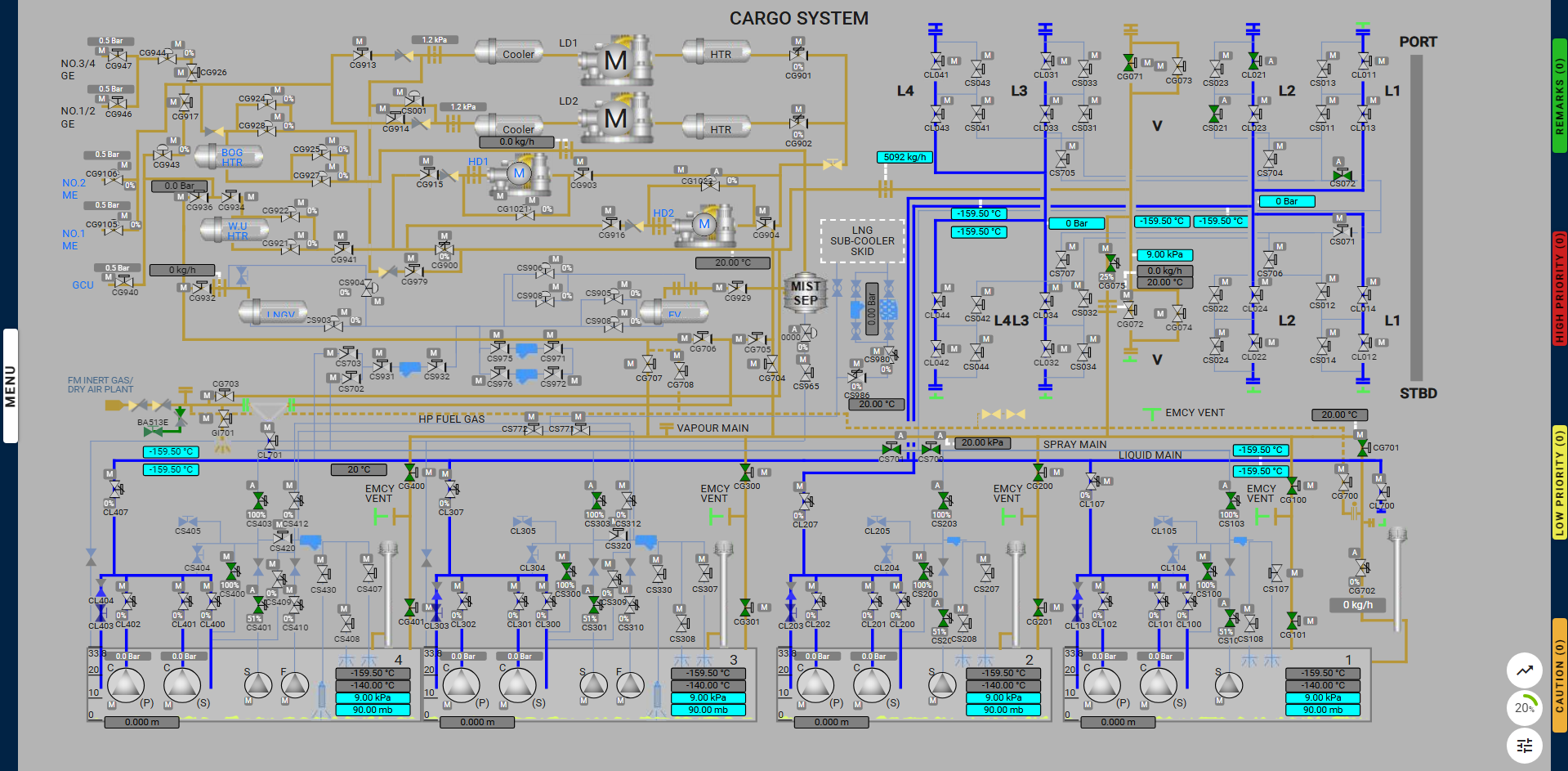
The stripping of cargo tanks is carried out when the vessel needs to discharge the entire cargo parcel from its cargo tanks. To achieve this, the vessel uses its spray pumps and runs them until the desired level is reached, ensuring the maximum liquid volume is discharged from the tank.
The use of spray pumps is preferred because they are lower-capacity pumps, suitable for handling lower liquid levels inside the cargo tanks. The stripping operation is also performed in preparation for an upcoming dry dock.
The purpose of stripping cargo tanks is the removal of the dead heel, leaving the cargo tanks as empty of LNG as possible. This can be achieved by using the stripping/spray pumps to strip out all the remaining LNG after the cargo pumps have been used to empty the cargo tanks as far as possible.
The stripping/spray pumps would generally be started before the cargo pumps are stopped and at a cargo tank level above the minimum stripping/spray pump start level. The stripping/spray pumps discharge to the spray line, to the stripping crossover, and then to the manifold to the terminal.
On some occasions, it may prove more effective to set the stripping/spray pumps to discharge into one cargo tank to consolidate the remaining LNG. The remaining cargo tank would continue using the cargo pump to discharge all the LNG to the terminal before this cargo tank stripping/spray pump continues to empty the final cargo tank.
The operation can be conducted either with or without vapour return and would normally be conducted in a similar manner to the main unloading operation with regard to vapour handling.
Learning Objectives for the Exercise
When planning an LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) discharging operation some potential learning objectives for a training program focused on the discharge of LNG (liquefied natural gas):
1. Understanding LNG Properties: Explain the physical and chemical properties of LNG, including its boiling point, density, and flammability.
2. Safety Procedures: Identify and apply safety protocols and emergency response procedures specific to LNG operations.
3. Discharge Process: Describe the step-by-step process of discharging LNG from a tanker to a storage facility.
4. Equipment Familiarization: Demonstrate knowledge of the equipment used during the LNG discharge process, including pumps, hoses, and vapor return systems.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Understand the relevant regulations and industry standards governing LNG discharge operations.
6. Environmental Considerations: Assess the environmental impact of LNG discharge and identify measures to minimize potential risks.
7. Monitoring and Control: Explain the monitoring systems in place to ensure safe and efficient LNG discharge, including temperature and pressure controls.
8. Incident Management: Recognize potential hazards during the LNG discharge process and develop strategies for risk mitigation and incident management.
9. Communication Skills: Demonstrate effective communication and coordination with team members and other stakeholders during the discharge operation.
10. Practical Application: Engage in hands-on training to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world LNG discharge scenarios.
|
Alarm Condition |
Alarm Time | Alarm Level | Alarm Title | Alarm Description |
Actions |
| Remark | Started Stripping | Stripping of Cargo Tanks has started, open master valves of remaining tanks and increase the discharge rate to required level. | |||
|
Tank level reaches 0.13 m |
caution | Throttle Discharge Valve CS101 | Please throttle discharge valve CS101 to stabilize the pump. | ||
|
Tank level reaches 0.13 m and pump unstable |
Low | Low Current | low current, adjust the discharge valve to make the pump stable. | ||
|
Tank Level 0.122 m and pump running or level overridden and Tank Level 0.110 m |
High | Spray pump in CT1 Tripped | Spray pump tripped due to tank reached low level, Close discharge valve CS101. |
If more than 2 pump tripped exercise will be terminated. |
|
|
when un necessary valve opened or required valve closed |
Caution | Deviation Detected | Deviation from the exercise is detected, undo your last action. |
Fails if that valve is not closed or opened within 1 minute |
Step By Step Procedure
| Valve Name | Status |
| CL021 | OPEN |
| CS021 | OPEN |
| CS101 | OPEN (25% ~ 30%) |
| CS103 | OPEN |
| CS201 | OPEN (25% ~ 30%) |
| CS203 | OPEN |
| CS301 | OPEN (25% ~ 30%) |
| CS303 | OPEN |
| CS401 | OPEN (25% ~ 30%) |
| CS403 | OPEN |
| CS701 | OPEN |
| CS700 | OPEN |
| CS072 | OPEN |
| CG702 | CLOSE & AUTO |
| CL031 | CLOSE |
| CL041 | CLOSE |
Pump Trips